Optimize Code for Reduction Operations by Using SIMD
This example shows how to generate optimized single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) code that performs reduction operations. A reduction is an operation that reduces a set of elements, such as an array, to a single value using an associative binary operator. For example, calculating the sum of the elements in an array is a reduction operation that uses the addition operator. For processors that support SIMD instructions, you can optimize reduction operations by generating parallel code that uses the SIMD instructions for the operation.
Example Model
Open the example model ex_rowmajor_algorithm. The model calculates the sum of the elements in a 4 by 3 by 2 array.
model = 'ex_rowmajor_algorithm';
open_system(model)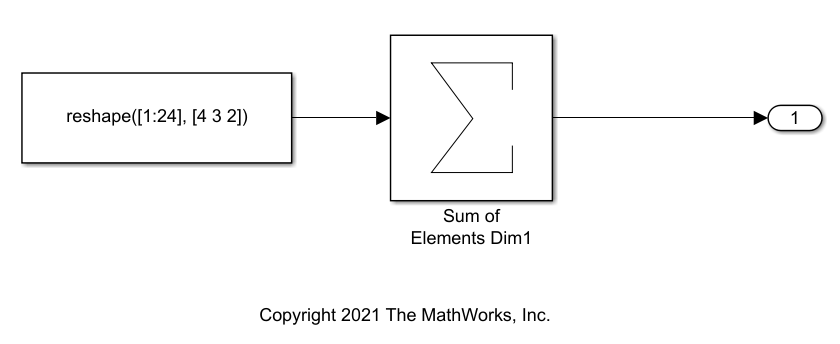
Generate SIMD Code Without Reduction Optimization
Open the configuration parameters for the model. On the Modeling tab, click Settings. On the Code Generation pane, set System target file to grt.tlc. On the Optimization pane, set the Leverage target hardware instruction set extensions to SSE2. Alternatively, use the command-line.
set_param(model, 'SystemTargetFile', 'grt.tlc'); set_param(model, 'SaveOutput', 'off'); set_param(model, 'RTWVerbose', 'off'); set_param(model, 'InstructionSetExtensions', 'SSE2');
De-select the parameter Optimize reductions.
set_param(model, 'OptimizeReductions', 'off');
Build the model.
slbuild(model);
### Searching for referenced models in model 'ex_rowmajor_algorithm'. ### Total of 1 models to build. ### Starting build procedure for: ex_rowmajor_algorithm ### Successful completion of build procedure for: ex_rowmajor_algorithm Build Summary Top model targets: Model Build Reason Status Build Duration ======================================================================================================================== ex_rowmajor_algorithm Information cache folder or artifacts were missing. Code generated and compiled. 0h 0m 10.019s 1 of 1 models built (0 models already up to date) Build duration: 0h 0m 10.431s
Inspect the generated ex_rowmajor_algorithm_step function.
file = fullfile('ex_rowmajor_algorithm_grt_rtw','ex_rowmajor_algorithm.c'); coder.example.extractLines(file,'/* Model step function */','/* End of Sum',1,1);
/* Model step function */
void ex_rowmajor_algorithm_step(void)
{
int32_T i;
/* Sum: '<Root>/Sum of Elements Dim1' incorporates:
* Constant: '<Root>/Constant1'
*/
ex_rowmajor_algorithm_Y.Out2 = -0.0F;
for (i = 0; i < 24; i++) {
ex_rowmajor_algorithm_Y.Out2 +=
ex_rowmajor_algorithm_ConstP.Constant1_Value[i];
}
The generated code contains a non-vectorized loop that adds each array element individually.
Generate SIMD Code With Reduction Optimization
Open the configuration parameters for the model. On the Modeling tab, click Settings. On the Optimization pane, set the Leverage target hardware instruction set extensions to SSE2. Alternatively, use the command-line.
set_param(model, 'InstructionSetExtensions', 'SSE2');
Select the parameter Optimize reductions.
set_param(model, 'OptimizeReductions', 'on'); set_param(model, 'MatFileLogging', 'off');
Build the model.
slbuild(model);
### Searching for referenced models in model 'ex_rowmajor_algorithm'. ### Total of 1 models to build. ### Starting build procedure for: ex_rowmajor_algorithm ### Successful completion of build procedure for: ex_rowmajor_algorithm Build Summary Top model targets: Model Build Reason Status Build Duration ==================================================================================================== ex_rowmajor_algorithm Generated code was out of date. Code generated and compiled. 0h 0m 8.2282s 1 of 1 models built (0 models already up to date) Build duration: 0h 0m 8.6217s
Inspect the generated ex_rowmajor_algorithm_step function.
file = fullfile('ex_rowmajor_algorithm_grt_rtw','ex_rowmajor_algorithm.c'); coder.example.extractLines(file,'/* Model step function */','/* Matfile',1,1);
/* Model step function */
void ex_rowmajor_algorithm_step(void)
{
__m128 tmp;
int32_T i;
real32_T tmp_0[4];
tmp = _mm_set1_ps(0.0F);
/* Sum: '<Root>/Sum of Elements Dim1' incorporates:
* Constant: '<Root>/Constant1'
*/
for (i = 0; i <= 20; i += 4) {
tmp = _mm_add_ps(tmp, _mm_loadu_ps
(&ex_rowmajor_algorithm_ConstP.Constant1_Value[i]));
}
/* End of Sum: '<Root>/Sum of Elements Dim1' */
_mm_storeu_ps(&tmp_0[0], tmp);
/* Outport: '<Root>/Out2' */
ex_rowmajor_algorithm_Y.Out2 = (tmp_0[0] + tmp_0[1]) + (tmp_0[2] + tmp_0[3]);
}
/* Model initialize function */
void ex_rowmajor_algorithm_initialize(void)
{
/* Registration code */
/* initialize error status */
rtmSetErrorStatus(ex_rowmajor_algorithm_M, (NULL));
/* external outputs */
ex_rowmajor_algorithm_Y.Out2 = 0.0F;
}
/* Model terminate function */
void ex_rowmajor_algorithm_terminate(void)
{
/* (no terminate code required) */
}
The vectorized loop uses the SSE2 function mm_add_ps, which adds four elements of the array to the sum in one step. This optimization improves the execution speed of the generated code.
Open the code generation report. On the C Code tab, click Open Report.

On the report summary, in the Additional Information section, the report indicates that reduction operations are optimized using the SSE2 instruction set.