Modulate and demodulate an audio signal with the FM broadcast modulator and demodulator System objects. Plot the frequency responses to compare the input and demodulated audio signals.
Load the audio file guitartune.wav by using an audio file reader System object™. Set the samples per frame to 44,100, which is large enough to include the entire audio file.
Create spectrum analyzer System objects to plot the spectra of the modulated and demodulated signals.
Create FM broadcast modulator and demodulator objects. Set the sample rate of the output audio signal to match the sample rate of the input audio signal. Configure the demodulator to match the specified modulator.
fmbDemod =
comm.FMBroadcastDemodulator with properties:
SampleRate: 200000
FrequencyDeviation: 75000
FilterTimeConstant: 7.5000e-05
AudioSampleRate: 44100
PlaySound: false
Stereo: false
RBDS: false
The length of the sequence input to the object must be an integer multiple of the decimation factor. To determine the audio decimation factor of the filter in the modulator and demodulator, use the info object function.
ans = struct with fields:
AudioDecimationFactor: 441
AudioInterpolationFactor: 2000
RBDSDecimationFactor: 19
RBDSInterpolationFactor: 320
ans = struct with fields:
AudioDecimationFactor: 50
AudioInterpolationFactor: 57
RBDSDecimationFactor: 50
RBDSInterpolationFactor: 57
The audio decimation factor of the modulator is a multiple of the audio frame length of 44,100. The audio decimation factor of the demodulator is an integer multiple of the 200,000 samples data sequence length of the modulator output.
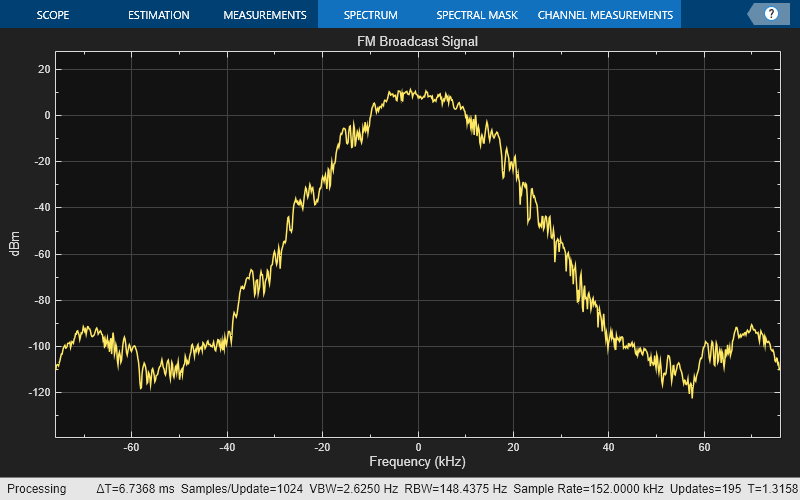
Modulate the audio signal and plot the spectrum of the modulated signal.
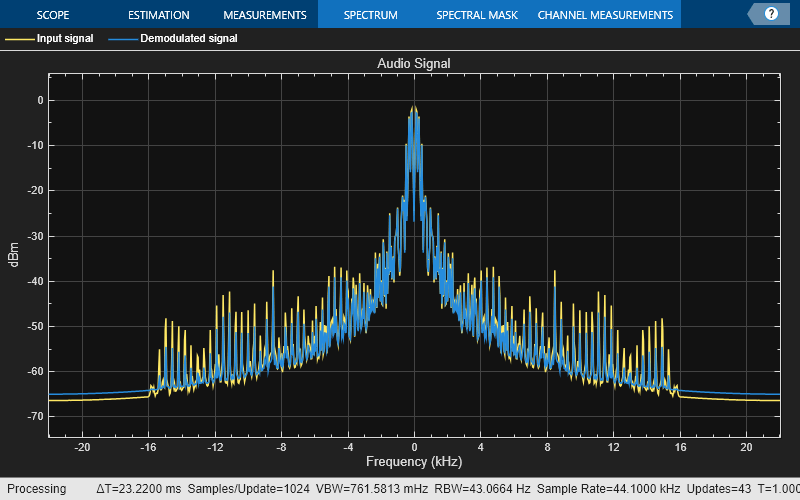
Demodulate the modulated audio signal and plot the resultant spectrum. Compare the input signal spectrum with the demodulated signal spectrum. The spectra are similar except that the demodulated signal has smaller high-frequency components.