UDP Receive
Receive UDP message from UDP host
Add-On Required: This feature requires the Simulink Coder Support Package for NXP FRDM-K64F Board add-on.
Libraries:
Simulink Coder Support Package for NXP FRDM-K64F Board
Description
The UDP Receive block receives UDP message from a UDP host.
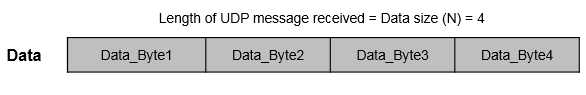
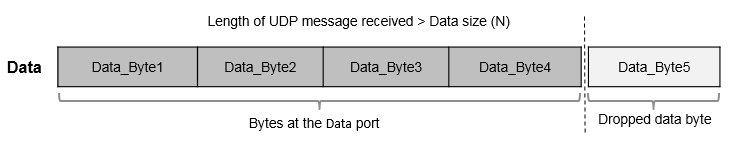
With each sample, the block outputs the data bytes of a UDP message as a data vector of the size that you specify in the Data size (N) parameter.
The block receives the message on the port number specified in the Local IP Port parameter. Match the port number specified in the Local IP Port parameter with the remote port number of the sending host.
You can choose to receive the UDP message in blocking or non-blocking mode.
Note
If you are having trouble using UDP to communicate with a computer, investigate if antivirus or firewall software is blocking UDP traffic. If so, try to configure the software to allow the traffic for a specific IP port number.
Ports
Output
Parameters
Version History
Introduced in R2017a