Validate Port Signals Among Ports of the Same Masked Block
This example shows how to create cross port constraints to validate compile-time signal attributes on ports of the same masked block. For example, you can set a constraint on the input and output port signals of the masked block so that they have the same data type. The rules for the cross port constraints are predefined. The available rules are Same Data Type, Same Dimension, and Same Complexity. Additionally, you can also set parameter conditions. Each port in the masked block is identified by a port identifier. The cross port constraint association is done through port identifiers.
Explore the Model
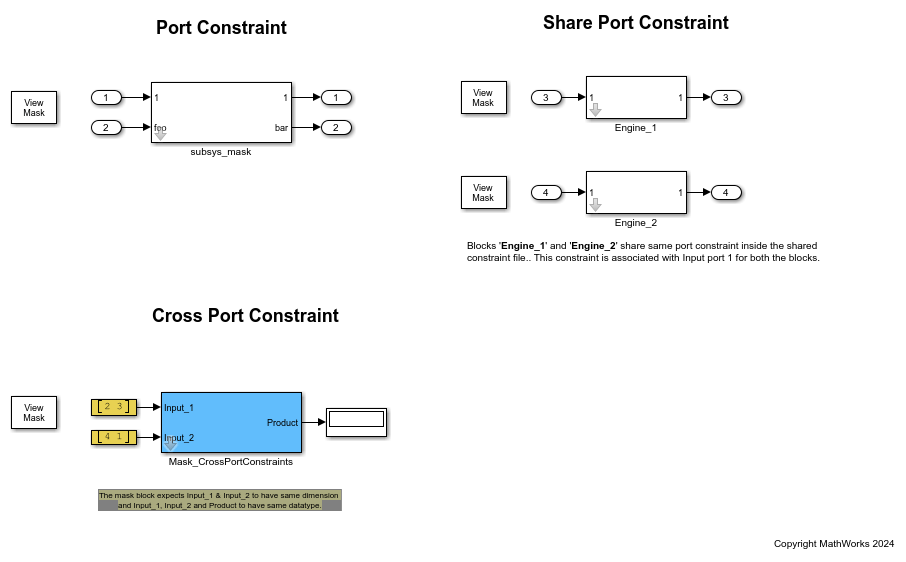
In this example model, refer to the block Mask_CrossPortConstraints that multiplies the input signals and displays the product in the output. This model uses the cross port constraint feature to check if the input and output port signals have same dimensions and datatypes. It has a subsystem block with two input ports and one output port. The input port identifiers are 1 and Input_2. The output port identifier is 1. The cross port constraints CheckDimensions and CheckDatatype are defined to validate the compile-time port signals of the input and output ports for same dimensions and same datatypes respectively.
open_system("slexMaskPortConstraints")
Create Port Identifiers
Create port identifiers to associate with the port constraint. Right-click Mask_CrossPortConstraints, then select Edit Mask. In the Mask Editor, select Constraints. On the toolstrip, click Port Identifiers. The Port Identifiers pane lists the port identifiers for the masked Subsystem block Mask_CrossPortConstraints.
1. Enter the Name for each input port as Input_1 and Input_2 and for the output port as Output_1.
The port name uniquely identifies the port in the mask. Multiple ports can have the same port identifier.
2. Select the Type of the port as either Input or Output.
3. Select the Identifier Type as name or index.
Select name if you want to identify the port using its name. Select index if you want to identify the port using its numerical port identifier.
4. In the Identifier(s) field, enter numerical port identifiers when Identifier Type is index, and enter port names when Identifier Type is name.

If you select name as the Identifier Type, then you do not need to select the Type, because each port name is unique.
Create Cross Port Constraints
To validate that input signals have the same dimension, create the cross-port constraint CheckDimensions. Go to Constraints > Cross Port. The port constraint appears in the Constraint Browser.
1. Specify the Constraint Name as CheckDimensions.
2. In Parameter Conditions, specify the Parameter Name as checkCrossPortDimensions and the Parameter Values as on.
3. In Rule, from the Rule list, select Same Dimension.
4. In Associations, click the Add button and select the Port Identifiers Input_1 and Input_2 to which you are associating the constraint.
5. In Diagnostics, from Diagnostic Level, to display an error or a warning message during compile time if the constraint is not satisfied.
6. In Diagnostics, set a Diagnostic Message that will be displayed if the cross port constraint validation fails.

Similarly, create another cross port constraints CheckDataType to validate that the ports Input_1, Input_2, and Output_1 have the same data type.

Validate Cross Port Constraints
Change the Dimension of the Input_1 and simulate the model.

The Diagnostic Viewer displays the following message.
The following two ports must have same dimensions. Caused by: Data at port 1 of block 'slexMaskCrossPortConstraints/Mask_CrossPortConstraints', which is '[1]' , must be the same as data at port 2 of block 'slexMaskCrossPortConstraints/Mask_CrossPortConstraints', which is '[2]'. 'The inputs to the masked block must be of same dimensions'.