refit
Refit neighborhood component analysis (NCA) model for classification
Description
mdlrefit = refit(mdl,Name=Value)mdl, with modified parameters specified by one
or more name-value arguments.
Examples
Generate checkerboard data using the generateCheckerBoardData.m function.
rng(2016,"twister"); % For reproducibility pps = 1375; [X,y] = generateCheckerBoardData(pps); X = X + 2;
Plot the data.
plot(X(y==1,1),X(y==1,2),"x") hold on plot(X(y==-1,1),X(y==-1,2),"x") hold off
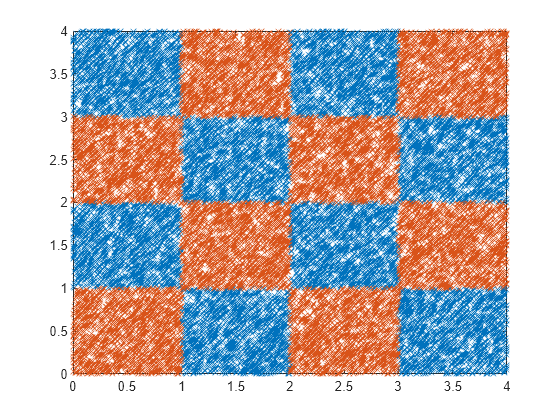
[n,p] = size(X)
n = 22000
p = 2
Add irrelevant predictors to the data.
Q = 98; Xrnd = unifrnd(0,4,n,Q); Xobs = [X,Xrnd];
This piece of code creates 98 additional predictors, all uniformly distributed between 0 and 4.
Partition the data into training and test sets. To create stratified partitions, so that each partition has similar proportion of classes, use y instead of length(y) as the partitioning criteria.
cvp = cvpartition(y,"Holdout",2000);cvpartition randomly chooses 2000 of the observations to add to the test set and the rest of the data to add to the training set. Create the training and validation sets using the assignments stored in the cvpartition object cvp.
Xtrain = Xobs(cvp.training(1),:); ytrain = y(cvp.training(1),:); Xval = Xobs(cvp.test(1),:); yval = y(cvp.test(1),:);
Compute the misclassification error without feature selection.
nca = fscnca(Xtrain,ytrain,FitMethod="none",Standardize=true, ... Solver="lbfgs"); loss_nofs = loss(nca,Xval,yval)
loss_nofs = 0.5165
The FitMethod="none" option uses the default weights (all 1s), which means all features are equally important.
This time, perform feature selection using neighborhood component analysis for classification, with .
w0 = rand(100,1); n = length(ytrain)
n = 20000
lambda = 1/n; nca = refit(nca,InitialFeatureWeights=w0,FitMethod="exact", ... Lambda=lambda,Solver="sgd");
Plot the objective function value versus the iteration number.
plot(nca.FitInfo.Iteration,nca.FitInfo.Objective,"o") hold on plot(nca.FitInfo.Iteration,movmean(nca.FitInfo.Objective,10),".-") hold off xlabel("Iteration number") ylabel("Objective value")
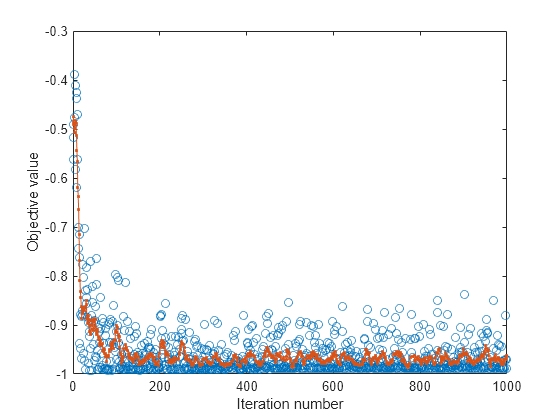
Compute the misclassification error with feature selection.
loss_withfs = loss(nca,Xval,yval)
loss_withfs = 0.0115
Plot the selected features.
semilogx(nca.FeatureWeights,"o") xlabel("Feature index") ylabel("Feature weight") grid on
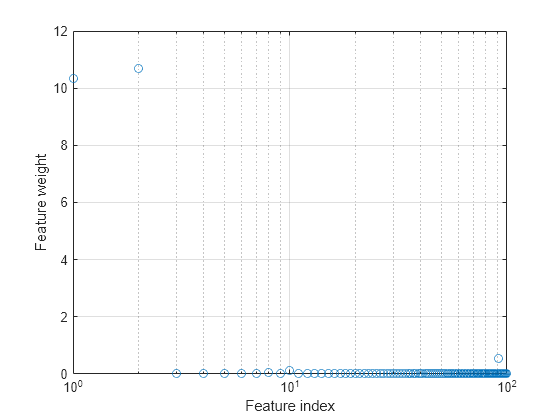
Select features using the feature weights and a relative threshold.
tol = 0.15; selidx = find(nca.FeatureWeights > tol*max(1,max(nca.FeatureWeights)))
selidx = 2×1
1
2
Feature selection improves the results and fscnca detects the correct two features as relevant.
Input Arguments
Neighborhood component analysis model or classification, specified
as a FeatureSelectionNCAClassification object.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: refit(mdl,Lambda=0.01) refits the model
mdl with a lambda value of
0.01.
Fitting Options
Method for fitting the model, specified as one of the following.
"exact"— Performs fitting using all of the data."none"— No fitting. Use this option to evaluate the generalization error of the NCA model using the initial feature weights supplied in the call tofscnca."average"— The function divides the data into partitions (subsets), fits each partition using theexactmethod, and returns the average of the feature weights. You can specify the number of partitions using theNumPartitionsname-value argument.
Example: FitMethod="none"
Regularization parameter, specified as a nonnegative scalar value.
For n observations, the best Lambda value
that minimizes the generalization error of the NCA model is expected
to be a multiple of 1/n
Example: Lambda=0.01
Data Types: double | single
Solver type for estimating feature weights, specified as one of the following.
"lbfgs"— Limited memory BFGS (Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno) algorithm (LBFGS algorithm)"sgd"— Stochastic gradient descent"minibatch-lbfgs"— Stochastic gradient descent with LBFGS algorithm applied to mini-batches
Example: Solver="minibatch-lbfgs"
Initial feature weights, specified as a p-by-1 vector of real positive scalar values.
Data Types: double | single
Indicator for verbosity level for the convergence summary display, specified as one of the following.
0 — No convergence summary
1 — Convergence summary including iteration number, norm of the gradient, and objective function value.
>1 — More convergence information depending on the fitting algorithm
When using solver
"minibatch-lbfgs"and verbosity level >1, the convergence information includes iteration log from intermediate mini-batch LBFGS fits.
Example: Verbose=2
Data Types: double | single
LBFGS or Mini-Batch LBFGS Options
Relative convergence tolerance on the gradient norm for solver lbfgs,
specified as a positive real scalar value.
Example: GradientTolerance=0.00001
Data Types: double | single
SGD or Mini-Batch LBFGS Options
Initial learning rate for solver sgd, specified as a positive scalar
value.
When using solver type "sgd", the learning rate decays over iterations
starting with the value specified for InitialLearningRate.
Example: InitialLearningRate=0.8
Data Types: double | single
Maximum number of passes for solver "sgd" (stochastic gradient
descent), specified as a positive integer value. Every pass processes
size(mdl.X,1) observations.
Example: PassLimit=10
Data Types: double | single
SGD or LBFGS or Mini-Batch LBFGS Options
Maximum number of iterations, specified as a positive integer.
Example: IterationLimit=250
Data Types: double | single
Output Arguments
Neighborhood component analysis model for classification, returned as a FeatureSelectionNCAClassification object. You
can either save the results as a new model or update the existing model as
mdl = refit(mdl,Name=Value).
Version History
Introduced in R2016b
See Also
FeatureSelectionNCAClassification | loss | fscnca | predict | selectFeatures
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)