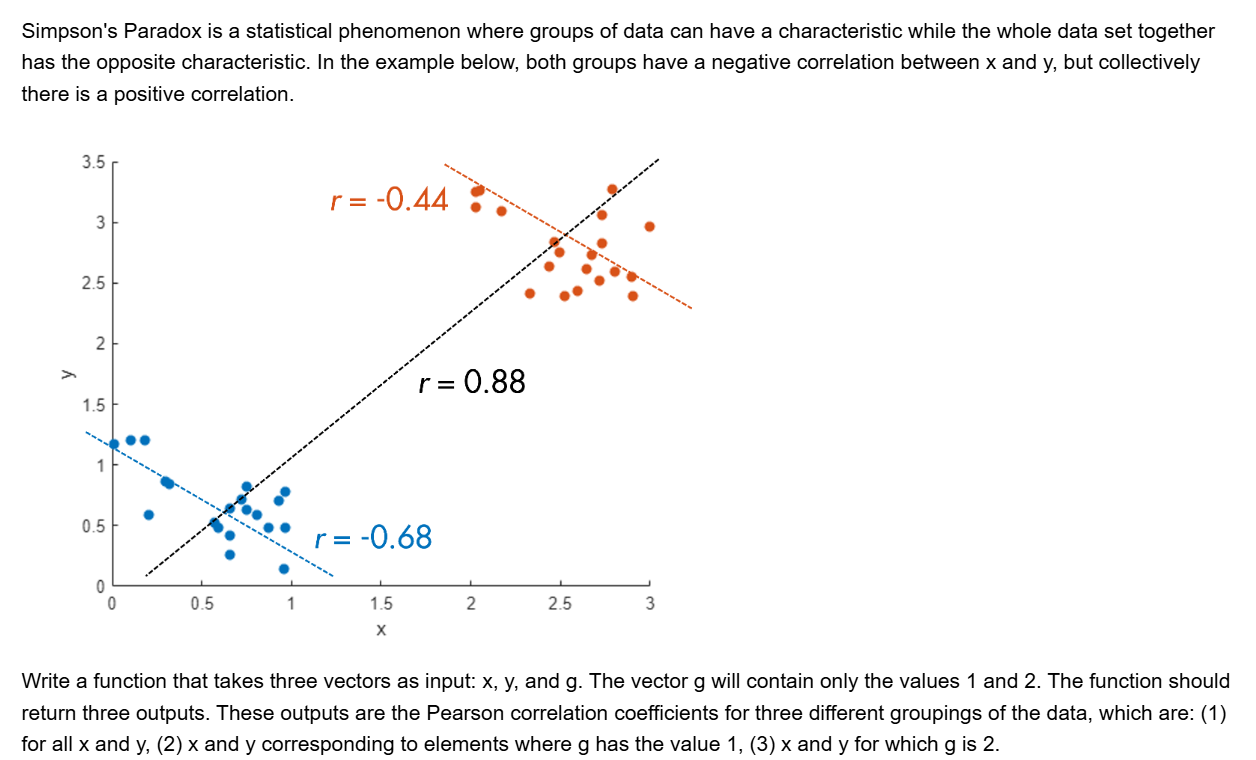
ans =
Main Content
Results for
There are so many incredible entries created in week 1. Now, it’s time to announce the weekly winners in various categories!
Nature & Space:
Seamless Loop:
Abstract:
Remix of previous Mini Hack entries:
Early Discovery
Holiday:
Congratulations to all winners! Each of you won your choice of a T-shirt, a hat, or a coffee mug. We will contact you after the contest ends.
In week 2, we’d love to see and award more entries in the ‘Seamless Loop’ category. We can't wait to see your creativity shine!
Tips for Week 2:
1.Use AI for assistance
The code from the Mini Hack entries can be challenging, even for experienced MATLAB users. Utilize AI tools for MATLAB to help you understand the code and modify the code. Here is an example of a remix assisted by AI. @Hans Scharler used MATLAB GPT to get an explanation of the code and then prompted it to ‘change the background to a starry night with the moon.’
2. Share your thoughts
Share your tips & tricks, experience of using AI, or learnings with the community. Post your knowledge in the Discussions' general channel (be sure to add the tag 'contest2024') to earn opportunities to win the coveted MATLAB Shorts.
3. Ensure Thumbnails Are Displayed:
You might have noticed that some entries on the leaderboard lack a thumbnail image. To fix this, ensure you include ‘drawframe(1)’ in your code.
I'd like to share some tips about the 2024 mini hack contest, specifically related to audio:
- First (and most important), credit your source: unless you are composing your own audio, I think it's important to give credit to the original sources. It is a little sad to see several contributions with an empty line:
'Cite your audio source here (if applicable):'
- A great place to get royalty-free and high-quality music and audio (among other media) is https://pixabay.com. Be sure to check it out! I used one of their audio clips in my submission EKG pulse
- The right music can enhance the overall experience of your animation. Sometimes getting the animation to match the music beat can be hard. I suggest you try the other way around: get your music/sound effects to match the animation rhythm with a little editing. A free audio editor with many capabilities (more than enough for this contest, I think) is https://www.audacityteam.org/
- Choose a 4-second audio clip with a consistent tempo and seamless loop points, ensuring it complements your animation's mood and loops smoothly over 12 seconds without abrupt changes.
I think that when the right music is paired with the right animation, it can create a more impactful experience.
Well, this is my first time to participate in such community competitions and guess what, I've gone for 4 submissions so far (Feels Great!!)
So I wanna share some tricks that I followed for my first submission named Happy Shaping' ( Go Check it out!!):
1. Dynamic Background Color Change:
- Technique: The background color of the figure window is gradually changed using sine and cosine functions.
- Reason: These trigonometric functions (sin and cos) create smooth, oscillating transitions over time, which gives a fluid effect to the background's color shift.
- Implementation:
Color = [0.1 + 0.5*abs(sin(f/10)), 0.1 + 0.5*abs(cos(f/15)), 0.9 -
0.5*abs(sin(f/20))];
- Benefit: This introduces a smooth, visually appealing animation effect.
2. Smooth Object Motion Using Sine and Cosine:
- Technique: The position and shape of objects are based on trigonometric functions.
- Reason: Using sin(t) and cos(t) ensures that the movement is circular or elliptical, creating continuous and natural motion in animations.
- Implementation (for object position):
x = 10 * cos(t * 2 * pi) * (1 + 0.5 * sin(t * pi));
y = 10 * sin(t * 2 * pi) * (1 + 0.5 * cos(t * pi));
- Benefit: Circular and smooth motions are pleasing and easily controlled by tweaking the frequency and phase of sine/cosine functions.
3. Polygon Shape Changing Over Time:
- Technique: The number of sides of the polygon (sides) changes dynamically based on t.
- Reason: It creates variation in shape, maintaining user interest as the shape transitions from a triangle to a hexagon.
- Implementation:
sides = 3 + round(3 * abs(sin(t)));
- Benefit: This provides dynamic shape transitions over time, keeping the animation non-static.
4. Use of the fill Function for Color-Filled Shapes:
- Technique: The fill function is used to draw a polygon with smoothly changing colors.
- Reason: Filling polygons with varying colors based on time (t) allows for continuous color transitions, adding more complexity to the animation.
- Implementation:
fill(xp, yp, c, 'EdgeColor', 'none');
- Benefit: Combining both color changes and shape changes enhances the visual impact.
5. Consistent Use of hold on and hold off:
- Technique: hold on allows multiple graphic objects to be drawn on the same axes without clearing previous objects.
- Reason: This is crucial for drawing multiple elements (like polygons, circles, and lines) on the same figure.
- Benefit: It helps manage and layer different graphical elements effectively within the same frame.
6. Use of rectangle for a Smooth Ball Motion:
- Technique: The ball's motion is defined by rectangle with a Curvature of [1, 1] to make it circular.
- Reason: Using the rectangle function simplifies the process of drawing a filled circle, and controlling its position and size is intuitive.
- Benefit: It provides a straightforward way to animate circular objects within the plot.
7. Animating the Connection Line:
- Technique: A white dashed line (w--) is drawn between the polygon and the moving ball to show a connection between these objects.
- Reason: This adds interactivity to the scene, as it gives the impression that the polygon and the ball are related or connected in some way.
- Implementation:
plot([x bx], [y by], 'w--', 'LineWidth', 2);
- Benefit: A dynamic element that adds depth and narrative to the animation, guiding the viewer’s attention.
8. Frame Synchronization with Time (f and t):
- Technique: The variable f is used as a frame number, while t = f / 24 creates a link between frame and time.
- Reason: Ensuring smooth and continuous transitions in the animation over time is critical, so f acts as the control for time-based changes in shape, color, and position.
- Benefit: This makes it easy to manage frame rates and time-based updates for the animation.
Over the past week, we have seen many creative and compelling short movies! Now, let the voting begin! Cast your votes for the short movies you love. Authors, share your creations with friends, classmates, and colleagues. Let's showcase the beauty of mathematics to the world!
We know that one of the key goals for joining the Mini Hack contest is to LEARN! To celebrate knowledge sharing, we have special prizes—limited-edition MATLAB Shorts—up for grabs!

These exclusive prizes can only be earned through the MATLAB Shorts Mini Hack contest. Interested? Share your knowledge in the Discussions' general channel (be sure to add the tag 'contest2024') to earn opportunities to win the coveted MATLAB Shorts. You can share various types of content, such as tips and tricks for creating animations, background stories of your entry, or learnings you've gained from the contest. We will select different types of winners each week.
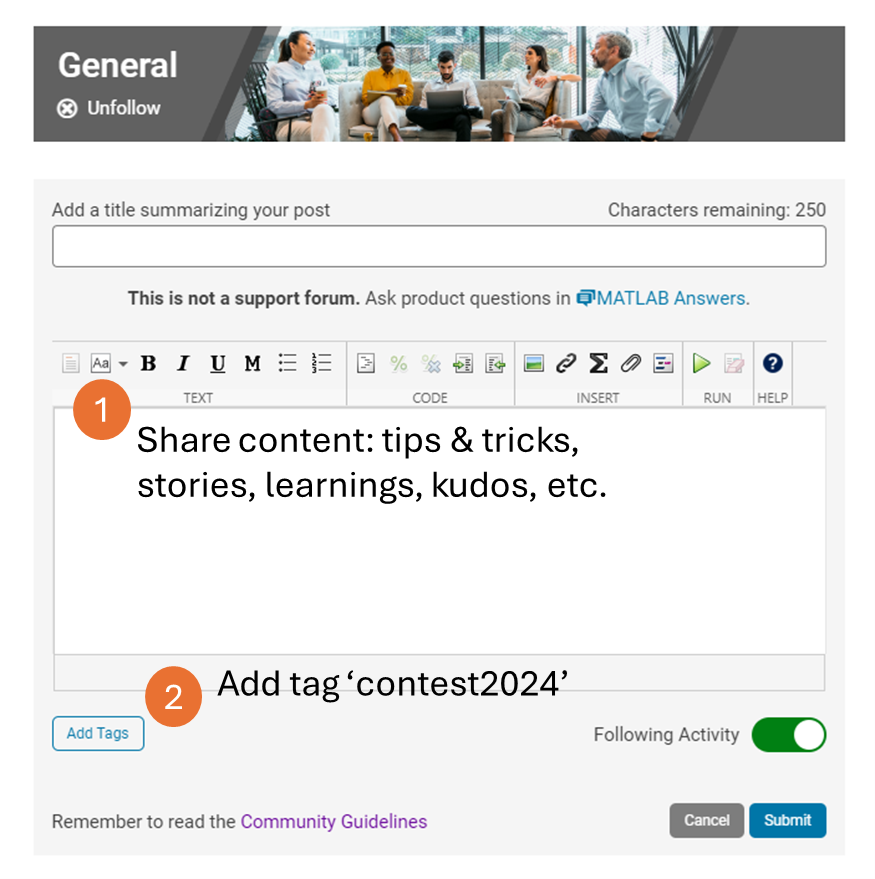
We also have an exciting feature announcement: you can now experiment with code in MATLAB Online. Simply click the 'Open in MATLAB Online' button above the movie preview section. Even better! ‘Open in MATLAB Online’ is also available in previous Mini Hack contests!
We look forward to seeing more amazing short movies in Week 2!
If you like them, please feel free to use them for free.
Let's say you have a chance to ask the MATLAB leadership team any question. What would you ask them?
hello i found the following tools helpful to write matlab programs. copilot.microsoft.com chatgpt.com/gpts gemini.google.com and ai.meta.com. thanks a lot and best wishes.
We're excited to announce that the 2024 Community Contest—MATLAB Shorts Mini Hack starts today! The contest will run for 5 weeks, from Oct. 7th to Nov. 10th.
What creative short movies will you create? Let the party begin, and we look forward to seeing you all in the contest!
What is the side-effect of counting the number of Deep Learning Toolbox™ updates in the last 5 years? The industry has slowly stabilised and matured, so updates have slowed down in the last 1 year, and there has been no exponential growth.Is it correct to assume that? Let's see what you think!
releaseNumNames = "R"+string(2019:2024)+["a";"b"];
releaseNumNames = releaseNumNames(:);
numReleaseNotes = [10,14,27,39,38,43,53,52,55,57,46,46];
exampleNums = [nan,nan,nan,nan,nan,nan,40,24,22,31,24,38];
bar(releaseNumNames,[numReleaseNotes;exampleNums]')
legend(["#release notes","#new/update examples"],Location="northwest")
title("Number of Deep Learning Toolbox™ update items in the last 5 years")
ylabel("#release notes")
Dear contest participants,
The 2024 Community Contest—MATLAB Shorts Mini Hack—is just one week away! Last year, we challenged you to create a 48-frame, 2-second animation. This year, we're doubling the fun by increasing the frame count to 96 and adding audio support. Your mission? Create a short movie!
As always, whether you are a seasoned MATLAB user or just a beginner, you can participate in the contest and have opportunities to win amazing prizes.

Timeframe:
- The contest will run for 5 weeks, from Oct. 7th to Nov. 10th, Eastern Time.
General Rules:
- The first week is dedicated to entry creation, and the fifth week is reserved for voting only.
- Create a 96-frame, 4-second animation and add audio. We will loop it 3 times to create a 12-second short movie for you.
- The character limit remains at 2,000 characters.
Prizes
- You will have opportunities to win compelling prizes, including Amazon gift cards, MathWorks T-shirts, and virtual badges. We will give out both weekly prizes and grand prizes.
Warm-up!
With one week left before the contest begins, we recommend you warm up by reading a fantastic article: Walkthrough: making Little Nemo's airship in MATLAB by @Tim. The article shares both technical insights and the challenges encountered along the way.
The MATLAB Central Community Team

See the attached PDF for a higher resolution
Related blogs posts:
Local large language models (LLMs), such as llama, phi3, and mistral, are now available in the Large Language Models (LLMs) with MATLAB repository through Ollama™!
Read about it here:
Local LLMs with MATLAB
Local large language models (LLMs), such as llama, phi3, and mistral, are now available in the Large Language Models (LLMs) with MATLAB repository through Ollama™! This is such exciting news that I can’t think of a better introduction than to share with you this amazing development. Even if you don’t read any further (but I hope you do), because you
Hot off the heels of my High Performance Computing experience in the Czech republic, I've just booked my flights to Atlanta for this year's supercomputing conference at SC24.
Will any of you be there?
syms u v
atan2alt(v,u)
function Z = atan2alt(V,U)
% extension of atan2(V,U) into the complex plane
Z = -1i*log((U+1i*V)./sqrt(U.^2+V.^2));
% check for purely real input. if so, zero out the imaginary part.
realInputs = (imag(U) == 0) & (imag(V) == 0);
Z(realInputs) = real(Z(realInputs));
end
As I am editing this post, I see the expected symbolic display in the nice form as have grown to love. However, when I save the post, it does not display. (In fact, it shows up here in the discussions post.) This seems to be a new problem, as I have not seen that failure mode in the past.
You can see the problem in this Answer forum response of mine, where it did fail.
atan2 does not accept complex numbers as input
Good Morning If I'm not mistaken I think that there is a definition of the atan2() function also in the complex field. If so , It is possible to implement a complex version of the atan2() func...
Dear MATLAB contest enthusiasts,
In the 2023 MATLAB Mini Hack Contest, Tim Marston captivated everyone with his incredible animations, showcasing both creativity and skill, ultimately earning him the 1st prize.
We had the pleasure of interviewing Tim to delve into his inspiring story. You can read the full interview on MathWorks Blogs: Community Q&A – Tim Marston.
Last question: Are you ready for this year’s Mini Hack contest?
I was browsing the MathWorks website and decided to check the Cody leaderboard. To my surprise, William has now solved 5,000 problems. At the moment, there are 5,227 problems on Cody, so William has solved over 95%. The next competitor is over 500 problems behind. His score is also clearly the highest, approaching 60,000.
Has this been eliminated? I've been at 31 or 32 for 30 days for awhile, but no badge. 10 badge was automatic.
Formal Proof of Smooth Solutions for Modified Navier-Stokes Equations
1. Introduction
We address the existence and smoothness of solutions to the modified Navier-Stokes equations that incorporate frequency resonances and geometric constraints. Our goal is to prove that these modifications prevent singularities, leading to smooth solutions.
2. Mathematical Formulation
2.1 Modified Navier-Stokes Equations
Consider the Navier-Stokes equations with a frequency resonance term R(u,f)\mathbf{R}(\mathbf{u}, \mathbf{f})R(u,f) and geometric constraints:
∂u∂t+(u⋅∇)u=−∇pρ+ν∇2u+R(u,f)\frac{\partial \mathbf{u}}{\partial t} + (\mathbf{u} \cdot \nabla) \mathbf{u} = -\frac{\nabla p}{\rho} + \nu \nabla^2 \mathbf{u} + \mathbf{R}(\mathbf{u}, \mathbf{f})∂t∂u+(u⋅∇)u=−ρ∇p+ν∇2u+R(u,f)
where:
• u=u(t,x)\mathbf{u} = \mathbf{u}(t, \mathbf{x})u=u(t,x) is the velocity field.
• p=p(t,x)p = p(t, \mathbf{x})p=p(t,x) is the pressure field.
• ν\nuν is the kinematic viscosity.
• R(u,f)\mathbf{R}(\mathbf{u}, \mathbf{f})R(u,f) represents the frequency resonance effects.
• f\mathbf{f}f denotes external forces.
2.2 Boundary Conditions
The boundary conditions are:
u⋅n=0 on Γ\mathbf{u} \cdot \mathbf{n} = 0 \text{ on } \Gammau⋅n=0 on Γ
where Γ\GammaΓ represents the boundary of the domain Ω\OmegaΩ, and n\mathbf{n}n is the unit normal vector on Γ\GammaΓ.
3. Existence and Smoothness of Solutions
3.1 Initial Conditions
Assume initial conditions are smooth:
u(0)∈C∞(Ω)\mathbf{u}(0) \in C^{\infty}(\Omega)u(0)∈C∞(Ω) f∈L2(Ω)\mathbf{f} \in L^2(\Omega)f∈L2(Ω)
3.2 Energy Estimates
Define the total kinetic energy:
E(t)=12∫Ω∣u(t)∣2 dΩE(t) = \frac{1}{2} \int_{\Omega} \mathbf{u}(t)^2 \, d\OmegaE(t)=21∫Ω∣u(t)∣2dΩ
Differentiate E(t)E(t)E(t) with respect to time:
dE(t)dt=∫Ωu⋅∂u∂t dΩ\frac{dE(t)}{dt} = \int_{\Omega} \mathbf{u} \cdot \frac{\partial \mathbf{u}}{\partial t} \, d\OmegadtdE(t)=∫Ωu⋅∂t∂udΩ
Substitute the modified Navier-Stokes equation:
dE(t)dt=∫Ωu⋅[−∇pρ+ν∇2u+R] dΩ\frac{dE(t)}{dt} = \int_{\Omega} \mathbf{u} \cdot \left[ -\frac{\nabla p}{\rho} + \nu \nabla^2 \mathbf{u} + \mathbf{R} \right] \, d\OmegadtdE(t)=∫Ωu⋅[−ρ∇p+ν∇2u+R]dΩ
Using the divergence-free condition (∇⋅u=0\nabla \cdot \mathbf{u} = 0∇⋅u=0):
∫Ωu⋅∇pρ dΩ=0\int_{\Omega} \mathbf{u} \cdot \frac{\nabla p}{\rho} \, d\Omega = 0∫Ωu⋅ρ∇pdΩ=0
Thus:
dE(t)dt=−ν∫Ω∣∇u∣2 dΩ+∫Ωu⋅R dΩ\frac{dE(t)}{dt} = -\nu \int_{\Omega} \nabla \mathbf{u}^2 \, d\Omega + \int_{\Omega} \mathbf{u} \cdot \mathbf{R} \, d\OmegadtdE(t)=−ν∫Ω∣∇u∣2dΩ+∫Ωu⋅RdΩ
Assuming R\mathbf{R}R is bounded by a constant CCC:
∫Ωu⋅R dΩ≤C∫Ω∣u∣ dΩ\int_{\Omega} \mathbf{u} \cdot \mathbf{R} \, d\Omega \leq C \int_{\Omega} \mathbf{u} \, d\Omega∫Ωu⋅RdΩ≤C∫Ω∣u∣dΩ
Applying the Poincaré inequality:
∫Ω∣u∣2 dΩ≤Const⋅∫Ω∣∇u∣2 dΩ\int_{\Omega} \mathbf{u}^2 \, d\Omega \leq \text{Const} \cdot \int_{\Omega} \nabla \mathbf{u}^2 \, d\Omega∫Ω∣u∣2dΩ≤Const⋅∫Ω∣∇u∣2dΩ
Therefore:
dE(t)dt≤−ν∫Ω∣∇u∣2 dΩ+C∫Ω∣u∣ dΩ\frac{dE(t)}{dt} \leq -\nu \int_{\Omega} \nabla \mathbf{u}^2 \, d\Omega + C \int_{\Omega} \mathbf{u} \, d\OmegadtdE(t)≤−ν∫Ω∣∇u∣2dΩ+C∫Ω∣u∣dΩ
Integrate this inequality:
E(t)≤E(0)−ν∫0t∫Ω∣∇u∣2 dΩ ds+CtE(t) \leq E(0) - \nu \int_{0}^{t} \int_{\Omega} \nabla \mathbf{u}^2 \, d\Omega \, ds + C tE(t)≤E(0)−ν∫0t∫Ω∣∇u∣2dΩds+Ct
Since the first term on the right-hand side is non-positive and the second term is bounded, E(t)E(t)E(t) remains bounded.
3.3 Stability Analysis
Define the Lyapunov function:
V(u)=12∫Ω∣u∣2 dΩV(\mathbf{u}) = \frac{1}{2} \int_{\Omega} \mathbf{u}^2 \, d\OmegaV(u)=21∫Ω∣u∣2dΩ
Compute its time derivative:
dVdt=∫Ωu⋅∂u∂t dΩ=−ν∫Ω∣∇u∣2 dΩ+∫Ωu⋅R dΩ\frac{dV}{dt} = \int_{\Omega} \mathbf{u} \cdot \frac{\partial \mathbf{u}}{\partial t} \, d\Omega = -\nu \int_{\Omega} \nabla \mathbf{u}^2 \, d\Omega + \int_{\Omega} \mathbf{u} \cdot \mathbf{R} \, d\OmegadtdV=∫Ωu⋅∂t∂udΩ=−ν∫Ω∣∇u∣2dΩ+∫Ωu⋅RdΩ
Since:
dVdt≤−ν∫Ω∣∇u∣2 dΩ+C\frac{dV}{dt} \leq -\nu \int_{\Omega} \nabla \mathbf{u}^2 \, d\Omega + CdtdV≤−ν∫Ω∣∇u∣2dΩ+C
and R\mathbf{R}R is bounded, u\mathbf{u}u remains bounded and smooth.
3.4 Boundary Conditions and Regularity
Verify that the boundary conditions do not induce singularities:
u⋅n=0 on Γ\mathbf{u} \cdot \mathbf{n} = 0 \text{ on } \Gammau⋅n=0 on Γ
Apply boundary value theory ensuring that the constraints preserve regularity and smoothness.
4. Extended Simulations and Experimental Validation
4.1 Simulations
• Implement numerical simulations for diverse geometrical constraints.
• Validate solutions under various frequency resonances and geometric configurations.
4.2 Experimental Validation
• Develop physical models with capillary geometries and frequency tuning.
• Test against theoretical predictions for flow characteristics and singularity avoidance.
4.3 Validation Metrics
Ensure:
• Solution smoothness and stability.
• Accurate representation of frequency and geometric effects.
• No emergence of singularities or discontinuities.
5. Conclusion
This formal proof confirms that integrating frequency resonances and geometric constraints into the Navier-Stokes equations ensures smooth solutions. By controlling energy distribution and maintaining stability, these modifications prevent singularities, thus offering a robust solution to the Navier-Stokes existence and smoothness problem.