Map Persistent Arrays and dsp.Delay Objects to RAM
Map persistent arrays and dsp.Delay objects to RAM on hardware to
reduce the area used on your target device. For more information on general RAM mapping,
see Apply RAM Mapping to Optimize Area.
Enable RAM Mapping
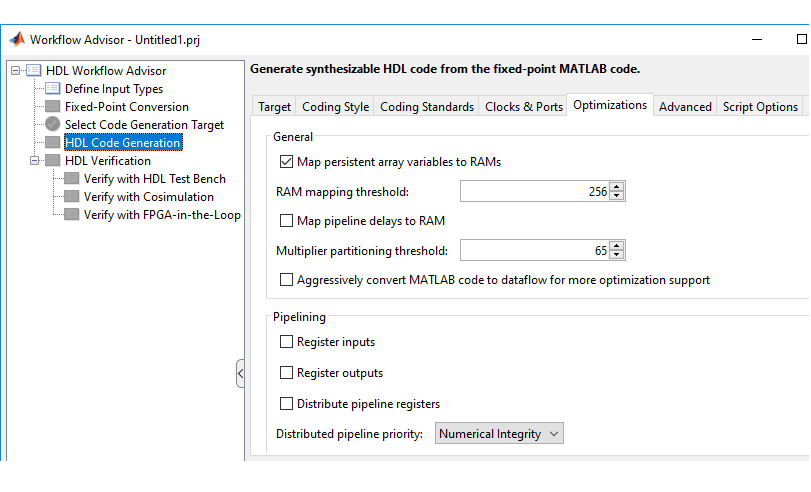
In the HDL Workflow Advisor, in the left pane, click HDL Workflow Advisor > HDL Code Generation. Then click the Optimizations tab.
Select Map persistent array variables to RAMs.
Set the RAM mapping threshold to either:
An integer that specifies the RAM size of the smallest persistent array, user-defined System object™ private property, or
dsp.Delayobject that you want to map to RAM.A string of format
MxNthat specifies two thresholds to define the shape of the data to map to RAM, whereMis the delay length (for delays) or array size (for persistent array variables) andNis the word length or bit width of the data type. Setting both thresholds excludes delays or persistent arrays from being mapped to RAM that inefficiently map to block RAM on your target hardware.
RAM Mapping Requirements for Persistent Arrays and System object Properties
The following table shows a summary of the RAM mapping behavior for persistent arrays and private properties of a user-defined System object.
| Map Persistent Array Variables to RAMs Setting | Mapping Behavior |
|---|---|
on | Map to RAM. For restrictions, see RAM Mapping Restrictions. |
off | Map to registers in the generated HDL code. |
RAM Mapping Restrictions
When you enable RAM mapping, a persistent array or user-defined System object private property maps to a block RAM when all of these conditions are true:
Each read or write access is for a single element only. For example, submatrix access and array copies are not supported.
Address computation logic is not read-dependent. For example, computation of a read or write address using the data read from the array is not supported.
Persistent variables or user-defined System object private properties are initialized to 0 if they have a cyclic dependency. For example, if you have two persistent variables, A and B, you have a cyclic dependency if A depends on B, and B depends on A.
If an access is within a conditional statement, the conditional statement uses only simple logic expressions (
&&,||,~) or relational operators. For example, in this code,r1does not map to RAM:if (mod(i,2) > 0) a = r1(u); else r1(i) = u; endYou can rewrite complex conditions, such as conditions that call functions, by assigning them to temporary variables, and using the temporary variables in the conditional statement. For example, to map
r1to RAM, rewrite the previous code as:temp = mod(i,2); if (temp > 0) a = r1(u); else r1(i) = u; endThe persistent array or user-defined System object private property value depends on external inputs.
For example, in the following code,
bigarraydoes not map to RAM because it does not depend onu:function z = foo(u) persistent cnt bigarray if isempty(cnt) cnt = fi(0,1,16,10,hdlfimath); bigarray = uint8(zeros(1024,1)); end z = u + cnt; idx = uint8(cnt); temp = bigarray(idx+1); cnt(:) = cnt + fi(1,1,16,0,hdlfimath) + temp; bigarray(idx+1) = idx;The RAM size is greater than or equal to the
RAMMappingThresholdvalue. The RAM size is the product ofArray Size * Word Length * Complexity, where:Array Sizeis the number of elements in the array.Word Lengthis the number of bits that represent the data type of the array.Complexityis 2 for a complex data type or 1 for a real datatype.
Access to the persistent variable that you are mapping to RAM is not in a loop, such as a
forloop, unless the loop is unrolled. For more information, seecoder.unroll.Access to the persistent variable that you are mapping to RAM is not in a nested conditional statement, such as a nested
ifstatement or nestedswitchstatement.
If any of the above conditions is false, the persistent array or user-defined System object private property maps to a register in the HDL code.
RAM Mapping Requirements for dsp.Delay System Objects
This table describes the dsp.Delay
System object RAM mapping behavior:
| Map Persistent Array Variables to RAMs Option | Mapping Behavior |
|---|---|
on | A
If any of the conditions
are false, the |
off | A |
RAM Mapping Comparison
hdl.RAM objects, dsp.Delay objects, persistent array variables, and user-defined
System object private properties can map to RAM, but have different attributes. This
table summarizes the differences.
| Attribute | hdl.RAM
Objects | dsp.Delay
Objects | Persistent Arrays and
User-Defined System object Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAM mapping criteria | Unconditionally maps to RAM | Maps to RAM in HDL code under specific conditions. See RAM Mapping Requirements for dsp.Delay System Objects. | Maps to RAM in HDL code under specific conditions. See RAM Mapping Requirements for Persistent Arrays and System object Properties. |
| Address generation and port mapping | User specified | Automatic | Automatic |
| Access scheduling | User specified | Automatically inferred | Automatically inferred |
| Overclocking | None | None | Local multirate, if the access schedule requires it. |
| Latency with respect to simulation in MATLAB®. | 0 | 0 | 2 cycles if local multirate; 1 cycle otherwise. |
| RAM type | User specified | Dual port | Dual port |