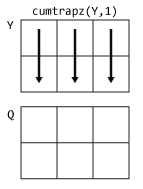
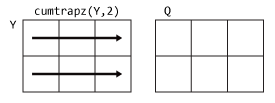
cumtrapz
Cumulative trapezoidal numerical integration
Description
Q = cumtrapz( computes the approximate
cumulative integral of Y)Y via the trapezoidal method with unit spacing. The size of Y
determines the dimension to integrate along:
If
Yis a vector, thencumtrapz(Y)is the cumulative integral ofY.If
Yis a matrix, thencumtrapz(Y)is the cumulative integral over each column.If
Yis a multidimensional array, thencumtrapz(Y)integrates over the first dimension whose size does not equal 1.
Q = cumtrapz(
integrates X,Y)Y with respect to the coordinates or scalar spacing
specified by X.
If
Xis a vector of coordinates, thenlength(X)must be equal to the size of the first dimension ofYwhose size does not equal 1.If
Xis a scalar spacing, thencumtrapz(X,Y)is equivalent toX*cumtrapz(Y).
Q = cumtrapz(___,
integrates along the dimension dim)dim using any of the previous
syntaxes. You must specify Y, and optionally can specify
X. If you specify X, then it can be a
scalar or a vector with length equal to size(Y,dim). For example,
if Y is a matrix, then cumtrapz(X,Y,2)
cumulatively integrates each row of Y.
Examples
Input Arguments
Tips
Use
trapzandcumtrapzto perform numerical integrations on discrete data sets. Useintegral,integral2, orintegral3instead if a functional expression for the data is available.trapzreduces the size of the dimension it operates on to 1, and returns only the final integration value.cumtrapzalso returns the intermediate integration values, preserving the size of the dimension it operates on.