expint
Exponential integral function
Syntax
Description
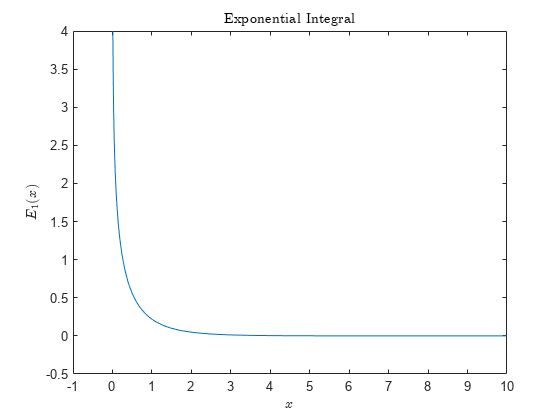
Y = expint(X)X.
Examples
Input Arguments
More About
References
[1] Abramowitz, M. and I. A. Stegun. Handbook of Mathematical Functions. Chapter 5, New York: Dover Publications, 1965.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced before R2006a