Configure Parameters for C Code Generation
When configuring a model for code generation, you can identify and configure parameters for tunability, for example for calibration. Types of parameters that you can configure are listed in this table.
| Type of Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Model parameter | Parameter defined within a model, such as a parameter in the model workspace. |
| External parameter | Parameter defined as an object in the base workspace or in a data dictionary. |
To configure a parameter for code generation, you must associate the parameter with a data object. For example, before configuring a MATLAB variable for code generation, in the Model Explorer, convert the variable to a parameter object.
When you open a model in the Simulink
Coder app, model
parameters that are associated with data objects appear in the Code Mappings
editor. In the editor, you can configure the parameters for code generation. If a model uses
external parameters, you can add them to the Code Mappings editor by clicking the
Refresh link to the right of the parameter name. That link initiates
an update diagram and, in the editor view, adds external parameters that are used by the
model.
Configure parameter data to:
Make the data accessible for interaction while the generated code executes.
Minimize the amount of data that is stored in memory.
Promote parameter data to the model interface so that other components and systems can access that data.
Improve readability and traceability of the generated code.
To control whether the parameters throughout a model are tunable, you can gain access to
model configuration parameter Default parameter behavior by using the
'Auto' will be tunable/inline link on the Code Mappings editor
Data Defaults tab. For example, you can use that link to make
parameters tunable in these cases:
Refine parameter settings during rapid prototyping
Calibrate parameters
Optimize parameters for production code
For code generation, examples show how to configure model parameters and model parameter
arguments for the model ConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface. You can configure code mappings by using the Code
Mappings Editor – C or code mappings programming interface (coder.mapping.api.CodeMapping).
Choose Customization Options for Parameters
By default, parameters in a model appear in generated code as fields of a global data structure named
model_P
Whether to set up a default configuration
If a model includes a significant number of parameters of a category that must be tunable (for example, more than 10), it is more efficient to configure the parameters of that category by using a default setting, and then override that setting for special cases. If the model includes a few parameters of a given category that have unique source, naming, or placement requirements, consider configuring the parameters individually.
How to declare and handle model parameter data in the generated code
As separate global variables
To read model parameter data from global variables defined in external code
As calls to access functions. Requires Embedded Coder®
For more information about these options, see Control Data and Function Interface in Generated Code.
Other considerations for model parameters include whether to:
Name parameters in the generated code by using parameter names in the model or by using unique code identifiers.
Support preprocessor conditionals defined by compiler flags or options. Requires Embedded Coder. See Compile Code Conditionally for Variations of Component Represented Using Variant Block.
Include the
statictype qualifier in global variable definitions and declarations, for example, to prevent name clashes. Requires Embedded Coder. See Prevent Name Clashes by Configuring Data Item as static (Embedded Coder).Include the
const,volatile, orconstandvolatiletype qualifier in global variable definitions and declarations. Requires Embedded Coder. See Protect Global Data with const and volatile Type Qualifiers (Embedded Coder).Generate a macro (
#define) or code that uses a macro defined in an external header file. Requires Embedded Coder. See Macro Definitions (#define) (Embedded Coder).Generate a global data structure with a name that you specify. Requires Embedded Coder. See Organize Data into Structures in Generated Code (Embedded Coder).
Place parameter data into a specific area of memory. Requires Embedded Coder. See Control Data and Function Placement in Memory by Inserting Pragmas (Embedded Coder).
For a list of interface requirements that are relevant to parameters that have corresponding storage classes and storage class properties, see Choose Storage Class and Storage Class Properties for Data Stores.
Parameter requirements for example model ConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface are:
By default, retain model parameters in the generated code for tuning. Do not optimize the code by inlining the parameters.
Apply prefix
mp_to names of variables that represent model parameters.
For this example, configure model parameters in ConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface to meet these code generation requirements.
Configure Default Code Generation Settings for Parameters
Default code generation settings for parameters can reduce the effort of preparing a model for code generation, especially if a model has a significant number of parameters with which you need to interact while the generated code executes. Choose configuration settings once, and the code generator applies those settings to parameters across the model. Simulink® stores the default configuration as part of the model.
Consider configuring default code generation settings for model parameters if your model uses multiple parameters for the same category that do not have unique requirements.
This example shows how to use the Code
Mappings Editor – C to configure default settings
for model parameters for the model ConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface. Configure model parameters so that they are
tunable and are defined and declared in the generated code as separate global
variables.
Open model
ConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface.openExample("ConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface")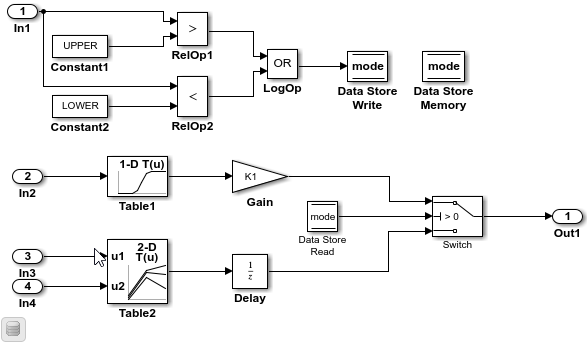
Open the Simulink Coder app.
In the C Code tab, select Code Interface > Default Code Mappings.
In the Code Mappings editor, under Parameters, select category Model parameters. Link text
'Auto' will be inlinedindicates that the code generator is configured to inline model parameters by default. A requirement for this example is model parameters be tunable. Click'Auto' will be inlined.In the Model Configuration Parameters dialog box, set model configuration parameter Default parameter behavior to
Tunable. Save the change and close the dialog box. In the Code Mappings editor, the link text changes to'Auto' will be tunable.In the Code Mappings, with the Model parameters category still selected, set the storage class to
ExportedGlobal.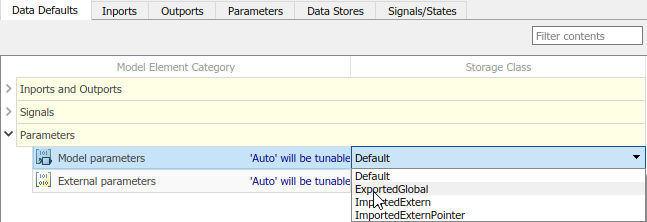
Save the model.
Configure Code Generation for Individual Parameters
You can configure individual parameters for code generation. For example, if a model has two parameters of the same category that have unique code generation requirements, configure the parameters individually. Or, if you configure default settings for a category of parameters, you can override those settings for specific parameters.
If your model meets at least one of these criteria, consider configuring code generation settings for parameters individually:
Uses multiple parameters of the same category that have unique source, naming, or placement requirements.
Uses a few parameters of the same category.
Has a default configuration for a category of parameters and you need to override the configuration for some specific parameters.
This example shows how to use the Code Mappings editor to apply your default storage
class setting for model parameters to parameters K1,
Table1, and Table2 in model ConfigurationInterface. You configure code identifiers for those
parameters. You can specify
code generation identifiers, for example for integration, without modifying the model
design.
If you have not already done so, complete the steps in Configure Default Code Generation Settings for Parameters.
Expand Model Parameters. By default, the storage class for each parameter is set to
Auto. Use the model default configuration, which specifies storage classExportedGlobal.To avoid optimizations and force the code generator to use the default configuration, set the storage class to
Model default.To override the default configuration, specify the storage class that meets the code generation requirements for that parameter.
In the Code Mappings editor, under Model Parameters, select parameters
K1,Table1, andTable2. Set the storage class toModel default: ExportedGlobal.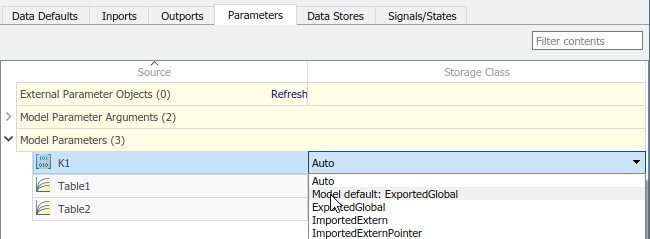
Configure the code identifiers for model parameters with names that include the prefix
mp_. In the Code Mappings editor, select model parameterK1. Click the icon and set the storage class property
Identifier to
icon and set the storage class property
Identifier to mp_K1. For parametersTable1andTable2, set Identifier tomp_Table1andmp_Table2.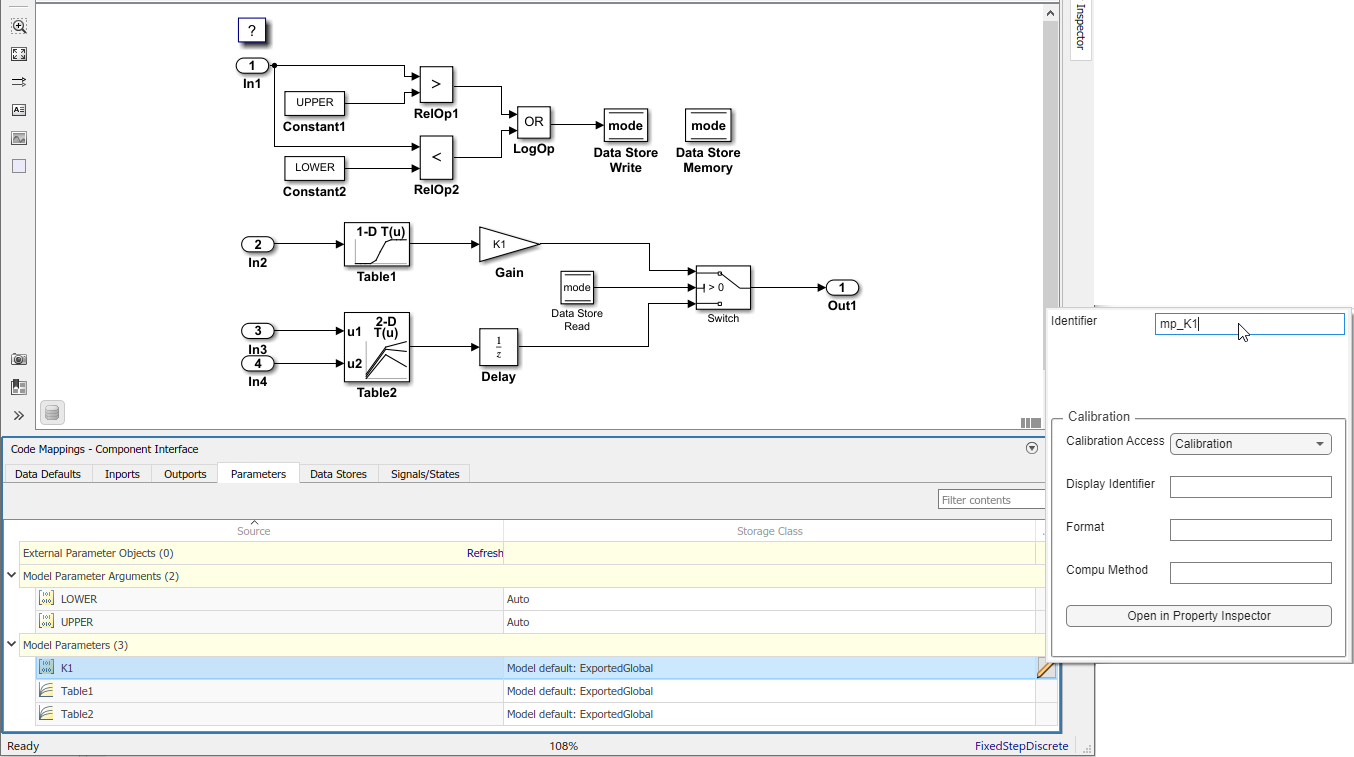
Save the model.
Generate and view the code. For example, find the data definitions for model parameter
mp_K1inConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface.c.int8_T mp_K1 = 2;
Find where the parameter is used in the step entry-point function.
if (mode) { output = (real_T)mp_K1 * dout_Table1; } else { output = dstate_X; }
Configure Code Generation Settings for Parameters Programmatically
To automate configuration of parameters for code generation, use the programming interface for code mappings. For example, when creating custom block libraries or part of an application test environment, use the programming interface to automate data configuration.
This example shows how to configure default settings for model parameters for model ConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface. Configure model parameters so that they are tunable
and are defined and declared in the generated code as separate global variables. Apply your default storage class
setting for model parameters to parameters K1,
Table1, and Table2. Configure code identifiers
for those parameters.
Open the example model.
openExample("ConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface")Set model configuration parameter Default parameter behavior to
Tunable.model = "ConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface"; set_param(model,"DefaultParameterBehavior","Tunable");
Create object
cmby calling functioncoder.mapping.api.get. The object stores the code generation configuration for data elements in modelConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface.cm = coder.mapping.api.get("ConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface");Configure default settings for model parameters by calling function
setDataDefault. For the arguments, specify these values:The object returned by
coder.mapping.api.getModelParametersfor the default categoryProperty name
StorageClasswith property valueExportedGlobal
setDataDefault(cm,"ModelParameters","StorageClass","ExportedGlobal");
Verify your default configuration for model parameters. Issue calls to
getDataDefaultthat specify the object returned bycoder.mapping.api.get, categoryModelParameters, andStorageClass.getDataDefault(cm,"ModelParameters","StorageClass")
ans = 'ExportedGlobal'Apply the default configuration for model parameters to parameters
K1,Table1, andTable2.By default, Simulink sets the storage class for individual parameters to
Auto. When the storage class isAuto, the code generator:Determines whether to eliminate the data from the generated code for optimization purposes.
If retaining the data, determines how to efficiently represent the data in the generated code, taking into account default configuration settings.
Configure the code generator to apply your default model parameter settings to parameters
K1,Table1, andTable2. For each parameter, call functionsetModelParameter. Specify the object returned bycoder.mapping.api.get, the parameter name, property nameStorageClass, and property valueModel default.setModelParameter(cm,"K1","StorageClass","Model default"); setModelParameter(cm,"Table1","StorageClass","Model default"); setModelParameter(cm,"Table2","StorageClass","Model default");
Verify your configuration changes for parameters
K1,Table1, andTable2by using calls to functiongetModelParameter.getModelParameter(cm,"K1","StorageClass")
ans = 'Model default'getModelParameter(cm,"Table1","StorageClass")
ans = 'Model default'getModelParameter(cm,"Table2","StorageClass")
ans = 'Model default'Configure code identifiers for the model parameters. For each parameter, call function
setModelParameter. Specify the object returned bycoder.mapping.api.get, the parameter name, property nameIdentifier, and one of these property values.Model Parameter Code Identifier K1mp_K1Table1mp_Table1Table2mp_Table2setModelParameter(cm,"K1","Identifier","mp_K1"); setModelParameter(cm,"Table1","Identifier","mp_Table1"); setModelParameter(cm,"Table2","Identifier","mp_Table2");
Verify your configuration changes for the model parameters by using calls to function
getModelParameter.getModelParameter(cm,"K1","Identifier")
ans = 'mp_K1'getModelParameter(cm,"Table1","Identifier")
ans = 'mp_Table1'getModelParameter(cm,"Table2","Identifier")
ans = 'mp_Table2'Save the model.
Generate and view the code. For example, find the data definitions for model parameter
mp_K1inConfigurationRapidPrototypingInterface.c.int8_T mp_K1 = 2;
Find where the parameter is used in the step entry-point function.
if (mode) { output = (real_T)mp_K1 * dout_Table1; } else { output = dstate_X; }
Choose Storage Class and Storage Class Properties for Model Parameters
Depending on your code generation requirements, choose from the list of available storage classes to configure code generation for model parameters.
Note
For constants, only the
Defaultstorage class applies.For model parameter arguments, only the
Auto,Default, andModel defaultstorage classes apply.Top-level models do not support individual mappings for model parameter arguments. If you select the
Autostorage class for a model parameter argument in a top-level model, the code generator inlines the argument.
| Requirements | Storage Class for Default Mappings | Storage Class for Individual Mappings |
|---|---|---|
| For data elements that cannot be optimized, represent data as a field of a standard data structure. | Default | |
| Enable optimizations, potentially generating more efficient code. | Auto | |
| Prevent optimizations from eliminating storage for a data element and use the default mapping for the data element category. | Model Default | |
| Generate standalone global variables. Generated code contains the variable declaration and definition. | ExportedGlobal | ExportedGlobal |
| Generate standalone global variables or global variable pointers. Generated code contains the variable or pointer declaration. Your external code provides the definition. | ImportedExtern, ImportedExternPointer | ImportedExtern, ImportedExternPointer |
The list of available storage classes might include other project-specific storage classes defined in an Embedded Coder Dictionary. If you have special requirements that are not met by the listed storage classes and you have Embedded Coder software, you can define a storage class. See Define Service Interfaces, Storage Classes, Memory Sections, and Function Templates for Software Architecture (Embedded Coder).
For an individual model parameter, use the Identifier storage class property to configure a name for the variable representing the parameter in the generated code.
See Also
Code
Mappings Editor – C | coder.mapping.api.CodeMapping