addOpening
Add signal to list of openings for slLinearizer or slTuner interface
Description
addOpening( adds
the specified point (signal) to the list of permanent openings for the s,pt)slLinearizer or slTuner interface, s.
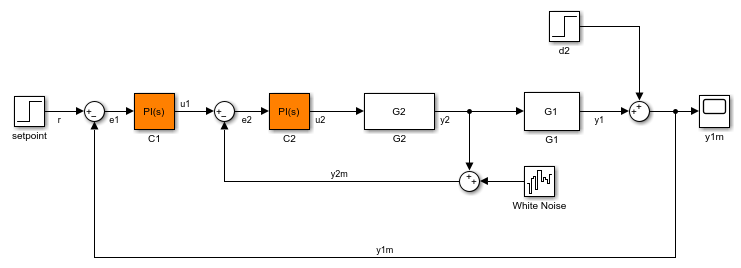
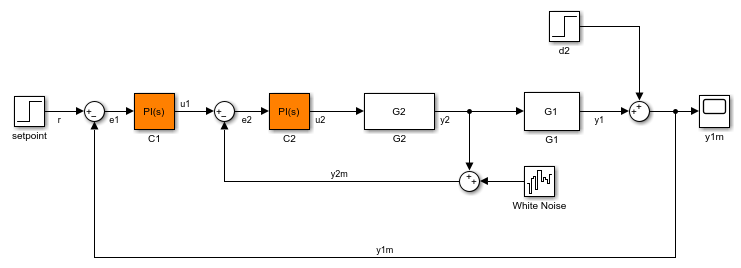
Use permanent openings to isolate a specific model component for the purposes of linearization and tuning. Suppose you have a large-scale model capturing aircraft dynamics and you want to perform linear analysis on the airframe only. You can use permanent openings to exclude all other components of the model. Another example is when you have cascaded loops within your model and you want to analyze a specific loop.
Examples
Input Arguments
More About
Version History
Introduced in R2013b
See Also
slLinearizer | slTuner | addPoint | addBlock | linio | removeOpening | removeAllOpenings