learnerCoderConfigurer
Create coder configurer of machine learning model
Syntax
Description
After training a machine learning model, create a coder configurer for the model
by using learnerCoderConfigurer. Use the object functions and properties
of the configurer to specify code generation options and to generate C/C++ code for the
predict and update functions of the machine
learning model. Generating C/C++ code requires MATLAB®
Coder™.
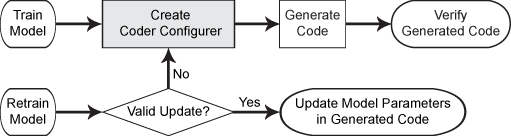
This flow chart shows the code generation workflow using a coder configurer. Use
learnerCoderConfigurer for the highlighted step.
configurer = learnerCoderConfigurer(Mdl,X)configurer for the machine learning model
Mdl. Specify the predictor data X for the
predict function of Mdl.
configurer = learnerCoderConfigurer(Mdl,X,Name,Value)predict function, the file name of generated C/C++ code, and the
verbosity level of the coder configurer.
Examples
Train a machine learning model, and then generate code for the predict and update functions of the model by using a coder configurer.
Load the carsmall data set and train a support vector machine (SVM) regression model.
load carsmall
X = [Horsepower,Weight];
Y = MPG;
Mdl = fitrsvm(X,Y);Mdl is a RegressionSVM object, which is a linear SVM model. The predictor coefficients in a linear SVM model provide enough information to predict responses for new observations. Removing the support vectors reduces memory usage in the generated code. Remove the support vectors from the linear SVM model by using the discardSupportVectors function.
Mdl = discardSupportVectors(Mdl);
Create a coder configurer for the RegressionSVM model by using learnerCoderConfigurer. Specify the predictor data X. The learnerCoderConfigurer function uses the input X to configure the coder attributes of the predict function input.
configurer = learnerCoderConfigurer(Mdl,X)
Warning: Default response is removed to support learnerCoderConfigurer. The model will predict NaNs for observations with missing values.
configurer =
RegressionSVMCoderConfigurer with properties:
Update Inputs:
Beta: [1×1 LearnerCoderInput]
Scale: [1×1 LearnerCoderInput]
Bias: [1×1 LearnerCoderInput]
Predict Inputs:
X: [1×1 LearnerCoderInput]
Code Generation Parameters:
NumOutputs: 1
OutputFileName: 'RegressionSVMModel'
Properties, Methods
configurer is a RegressionSVMCoderConfigurer object, which is a coder configurer of a RegressionSVM object.
To generate C/C++ code, you must have access to a C/C++ compiler that is configured properly. MATLAB Coder locates and uses a supported, installed compiler. You can use mex -setup to view and change the default compiler. For more details, see Change Default Compiler.
Generate code for the predict and update functions of the SVM regression model (Mdl) with default settings.
generateCode(configurer)
generateCode creates these files in output folder: 'initialize.m', 'predict.m', 'update.m', 'RegressionSVMModel.mat' Code generation successful.
The generateCode function completes these actions:
Generate the MATLAB files required to generate code, including the two entry-point functions
predict.mandupdate.mfor thepredictandupdatefunctions ofMdl, respectively.Create a MEX function named
RegressionSVMModelfor the two entry-point functions.Create the code for the MEX function in the
codegen\mex\RegressionSVMModelfolder.Copy the MEX function to the current folder.
Display the contents of the predict.m, update.m, and initialize.m files by using the type function.
type predict.mfunction varargout = predict(X,varargin) %#codegen
% Autogenerated by MATLAB, 13-Feb-2026 23:46:20
[varargout{1:nargout}] = initialize('predict',X,varargin{:});
end
type update.mfunction update(varargin) %#codegen
% Autogenerated by MATLAB, 13-Feb-2026 23:46:20
initialize('update',varargin{:});
end
type initialize.mfunction [varargout] = initialize(command,varargin) %#codegen
% Autogenerated by MATLAB, 13-Feb-2026 23:46:20
coder.inline('always')
persistent model
if isempty(model)
model = loadLearnerForCoder('RegressionSVMModel.mat');
end
switch(command)
case 'update'
% Update struct fields: Beta
% Scale
% Bias
model = update(model,varargin{:});
case 'predict'
% Predict Inputs: X
X = varargin{1};
if nargin == 2
[varargout{1:nargout}] = predict(model,X);
else
PVPairs = cell(1,nargin-2);
for i = 1:nargin-2
PVPairs{1,i} = varargin{i+1};
end
[varargout{1:nargout}] = predict(model,X,PVPairs{:});
end
end
end
Train an SVM model using a partial data set and create a coder configurer for the model. Use the properties of the coder configurer to specify coder attributes of the SVM model parameters. Use the object function of the coder configurer to generate C code that predicts labels for new predictor data. Then retrain the model using the whole data set and update parameters in the generated code without regenerating the code.
Train Model
Load the ionosphere data set. This data set has 34 predictors and 351 binary responses for radar returns, either bad ('b') or good ('g').
load ionosphereTrain a binary SVM classification model using the first 50 observations and a Gaussian kernel function with an automatic kernel scale.
Mdl = fitcsvm(X(1:50,:),Y(1:50), ... 'KernelFunction','gaussian','KernelScale','auto');
Mdl is a ClassificationSVM object.
Create Coder Configurer
Create a coder configurer for the ClassificationSVM model by using learnerCoderConfigurer. Specify the predictor data X in matrix format. Note that the learnerCoderConfigurer function does not support the table format for predictor data. The learnerCoderConfigurer function uses the input X to configure the coder attributes of the predict function input. Also, set the number of outputs to 2 so that the generated code returns predicted labels and scores.
configurer = learnerCoderConfigurer(Mdl,X(1:50,:),'NumOutputs',2);configurer is a ClassificationSVMCoderConfigurer object, which is a coder configurer of a ClassificationSVM object.
Specify Coder Attributes of Parameters
Specify the coder attributes of the SVM classification model parameters so that you can update the parameters in the generated code after retraining the model. This example specifies the coder attributes of predictor data that you want to pass to the generated code and the coder attributes of the support vectors of the SVM model.
First, specify the coder attributes of X so that the generated code accepts any number of observations. Modify the SizeVector and VariableDimensions attributes. The SizeVector attribute specifies the upper bound of the predictor data size, and the VariableDimensions attribute specifies whether each dimension of the predictor data has a variable size or fixed size.
configurer.X.SizeVector = [Inf 34]; configurer.X.VariableDimensions = [true false];
The size of the first dimension is the number of observations. In this case, the code specifies that the upper bound of the size is Inf and the size is variable, meaning that X can have any number of observations. This specification is convenient if you do not know the number of observations when generating code.
The size of the second dimension is the number of predictor variables. This value must be fixed for a machine learning model. X contains 34 predictors, so the value of the SizeVector attribute must be 34 and the value of the VariableDimensions attribute must be false.
If you retrain the SVM model using new data or different settings, the number of support vectors can vary. Therefore, specify the coder attributes of SupportVectors so that you can update the support vectors in the generated code.
configurer.SupportVectors.SizeVector = [250 34];
SizeVector attribute for Alpha has been modified to satisfy configuration constraints. SizeVector attribute for SupportVectorLabels has been modified to satisfy configuration constraints.
configurer.SupportVectors.VariableDimensions = [true false];
VariableDimensions attribute for Alpha has been modified to satisfy configuration constraints. VariableDimensions attribute for SupportVectorLabels has been modified to satisfy configuration constraints.
If you modify the coder attributes of SupportVectors, then the software modifies the coder attributes of Alpha and SupportVectorLabels to satisfy configuration constraints. If the modification of the coder attributes of one parameter requires subsequent changes to other dependent parameters to satisfy configuration constraints, then the software changes the coder attributes of the dependent parameters.
Generate Code
To generate C/C++ code, you must have access to a C/C++ compiler that is configured properly. MATLAB Coder locates and uses a supported, installed compiler. You can use mex -setup to view and change the default compiler. For more details, see Change Default Compiler.
Use generateCode to generate code for the predict and update functions of the SVM classification model (Mdl) with default settings.
generateCode(configurer)
generateCode creates these files in output folder: 'initialize.m', 'predict.m', 'update.m', 'ClassificationSVMModel.mat' Code generation successful.
generateCode generates the MATLAB files required to generate code, including the two entry-point functions predict.m and update.m for the predict and update functions of Mdl, respectively. Then generateCode creates a MEX function named ClassificationSVMModel for the two entry-point functions in the codegen\mex\ClassificationSVMModel folder and copies the MEX function to the current folder.
Verify Generated Code
Pass some predictor data to verify whether the predict function of Mdl and the predict function in the MEX function return the same labels. To call an entry-point function in a MEX function that has more than one entry point, specify the function name as the first input argument.
[label,score] = predict(Mdl,X);
[label_mex,score_mex] = ClassificationSVMModel('predict',X);Compare label and label_mex by using isequal.
isequal(label,label_mex)
ans = logical
1
isequal returns logical 1 (true) if all the inputs are equal. The comparison confirms that the predict function of Mdl and the predict function in the MEX function return the same labels.
score_mex might include round-off differences compared with score. In this case, compare score_mex and score, allowing a small tolerance.
find(abs(score-score_mex) > 1e-8)
ans = 0×1 empty double column vector
The comparison confirms that score and score_mex are equal within the tolerance 1e–8.
Retrain Model and Update Parameters in Generated Code
Retrain the model using the entire data set.
retrainedMdl = fitcsvm(X,Y, ... 'KernelFunction','gaussian','KernelScale','auto');
Extract parameters to update by using validatedUpdateInputs. This function detects the modified model parameters in retrainedMdl and validates whether the modified parameter values satisfy the coder attributes of the parameters.
params = validatedUpdateInputs(configurer,retrainedMdl);
Update parameters in the generated code.
ClassificationSVMModel('update',params)Verify Generated Code
Compare the outputs from the predict function of retrainedMdl and the predict function in the updated MEX function.
[label,score] = predict(retrainedMdl,X);
[label_mex,score_mex] = ClassificationSVMModel('predict',X);
isequal(label,label_mex)ans = logical
1
find(abs(score-score_mex) > 1e-8)
ans = 0×1 empty double column vector
The comparison confirms that labels and labels_mex are equal, and the score values are equal within the tolerance.
Input Arguments
Machine learning model, specified as a full or compact model object, as given in this table of supported models.
| Model | Full/Compact Model Object | Training Function |
|---|---|---|
| Binary decision tree for multiclass classification | ClassificationTree, CompactClassificationTree | fitctree |
| SVM for one-class and binary classification | ClassificationSVM, CompactClassificationSVM | fitcsvm |
| Linear model for binary classification | ClassificationLinear | fitclinear |
| Multiclass model for SVMs and linear models | ClassificationECOC, CompactClassificationECOC | fitcecoc |
| Binary decision tree for regression | RegressionTree, CompactRegressionTree | fitrtree |
| Support vector machine (SVM) regression | RegressionSVM, CompactRegressionSVM | fitrsvm |
| Linear regression | RegressionLinear | fitrlinear |
For the code generation usage notes and limitations of a machine learning model, see the Code Generation section of the model object page.
Predictor data for the predict function of
Mdl, specified as an n-by-p
numeric matrix, where n is the number of observations and
p is the number of predictor variables. To instead specify
X as a p-by-n matrix, where
the observations correspond to columns, you must set the 'ObservationsIn' name-value pair argument to 'columns'.
This option is available only for linear models and ECOC models with linear binary
learners.
Note that learnerCoderConfigurer does not support the table
data format for predictor data.
The predict function of a machine learning model predicts
labels for classification and responses for regression for given predictor data. After
creating the coder configurer configurer, you can use the generateCode
function to generate C/C++ code for the predict function of
Mdl. The generated code accepts predictor data that has the same
size and data type of X. You can specify whether each dimension has
a variable size or fixed size after creating configurer.
For example, if you want to generate C/C++ code that predicts labels using 100
observations with three predictor variables, then specify X as
zeros(100,3). The learnerCoderConfigurer
function uses only the size and data type of X, not its values.
Therefore, X can be predictor data or a MATLAB expression that represents the set of values with a certain data type. The
output configurer stores the size and data type of
X in the X property of
configurer. You can modify the size and data type of
X after creating configurer. For example,
change the number of observations to 200 and the data type to
single.
configurer.X.SizeVector = [200 3];
configurer.X.DataType = 'single';To allow the generated C/C++ code to accept predictor data with up to 100
observations, specify X as zeros(100,3) and
change the VariableDimensions
property.
configurer.X.VariableDimensions = [1 0];
[1
0] indicates that the first dimension of X (number of
observations) has a variable size and the second dimension of X
(number of predictor variables) has a fixed size. The specified number of observations,
100 in this example, becomes the maximum allowed number of observations in the generated
C/C++ code. To allow any number of observations, specify the bound as
Inf.configurer.X.SizeVector = [Inf 3];
Data Types: single | double
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: configurer =
learnerCoderConfigurer(Mdl,X,'NumOutputs',2,'OutputFileName','myModel') sets the
number of outputs in predict to 2 and specifies the file name
'myModel' for the generated C/C++ code.
Number of output arguments in the predict function of the
machine learning model Mdl, specified as the comma-separated pair
consisting of 'NumOutputs' and a positive integer
n.
This table lists the outputs for the predict function of
different models. predict in the generated C/C++ code returns the
first n outputs of the predict function in the
order given in the Outputs column.
| Model | predict Function of Model | Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Binary decision tree for multiclass classification | predict | label (predicted class
labels), score (posterior
probabilities), node (node numbers for
predicted classes), cnum (class numbers of
predicted labels) |
| SVM for one-class and binary classification | predict | label (predicted class labels), score (scores or posterior probabilities) |
| Linear model for binary classification | predict | Label (predicted class
labels), Score (classification
scores) |
| Multiclass model for SVMs and linear models | predict | label (predicted class labels), NegLoss (negated average
binary losses), PBScore (positive-class scores) |
| Binary decision tree for regression | predict | Yfit (predicted
responses), node (node numbers for
predictions) |
| SVM regression | predict | yfit (predicted
responses) |
| Linear regression | predict | YHat (predicted
responses) |
For example, if you specify 'NumOutputs',1 for an
SVM classification model, then predict returns predicted class
labels in the generated C/C++ code.
After creating the coder configurer configurer, you can
modify the number of outputs by using dot
notation.
configurer.NumOutputs = 2;
The 'NumOutputs' name-value pair argument is equivalent to
the '-nargout' compiler option of codegen (MATLAB Coder). This option specifies the number of output arguments in the
entry-point function of code generation. The object function generateCode of a coder configurer generates two entry-point
functions—predict.m and update.m for the
predict and update functions of
Mdl, respectively—and generates C/C++ code for the two
entry-point functions. The specified value for 'NumOutputs'
corresponds to the number of output arguments in predict.m.
Example: 'NumOutputs',2
Data Types: single | double
File name of the generated C/C++ code, specified as the comma-separated pair
consisting of 'OutputFileName' and a character vector or string
scalar.
The object function generateCode of a coder configurer generates C/C++ code using this file
name.
The file name must not contain spaces because they can lead to code generation failures in certain operating system configurations. Also, the name must be a valid MATLAB function name.
The default file name is the object name of Mdl followed by
'Model'. For example, if Mdl is a
CompactClassificationSVM or ClassificationSVM
object, then the default name is 'ClassificationSVMModel'.
After creating the coder configurer configurer, you can
modify the file name by using dot
notation.
configurer.OutputFileName = 'myModel';Example: 'OutputFileName','myModel'
Data Types: char | string
Verbosity level, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of
'Verbose' and either true (logical 1) or
false (logical 0). The verbosity level controls the display of
notification messages at the command line for the coder configurer
configurer.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
true (logical 1) | The software displays notification messages when your changes to the coder attributes of a parameter result in changes for other dependent parameters. |
false (logical
0) | The software does not display notification messages. |
To enable updating machine learning model parameters in the generated code, you need to configure the coder attributes of the parameters before generating code. The coder attributes of parameters are dependent on each other, so the software stores the dependencies as configuration constraints. If you modify the coder attributes of a parameter by using a coder configurer, and the modification requires subsequent changes to other dependent parameters to satisfy configuration constraints, then the software changes the coder attributes of the dependent parameters. The verbosity level determines whether or not the software displays notification messages for these subsequent changes.
After creating the coder configurer configurer, you can modify the
verbosity level by using dot
notation.
configurer.Verbose = false;
Example: 'Verbose',false
Data Types: logical
Predictor data observation dimension, specified as the comma-separated pair
consisting of 'ObservationsIn' and either 'rows'
or 'columns'. If you set 'ObservationsIn' to
'columns', then the predictor data X must be
oriented so that the observations correspond to columns.
Note
The 'columns' option is available only for linear models and
ECOC models with linear binary learners.
Example: 'ObservationsIn','columns'
Output Arguments
Coder configurer of a machine learning model, returned as one of the coder configurer objects in this table.
| Model | Coder Configurer Object |
|---|---|
| Binary decision tree for multiclass classification | ClassificationTreeCoderConfigurer |
| SVM for one-class and binary classification | ClassificationSVMCoderConfigurer |
| Linear model for binary classification | ClassificationLinearCoderConfigurer |
| Multiclass model for SVMs and linear models | ClassificationECOCCoderConfigurer |
| Binary decision tree for regression | RegressionTreeCoderConfigurer |
| Support vector machine (SVM) regression | RegressionSVMCoderConfigurer |
| Linear regression | RegressionLinearCoderConfigurer |
Use the object functions and properties of a coder configurer object to configure
code generation options and to generate C/C++ code for the predict
and update functions of the machine learning model.
Version History
Introduced in R2018b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)