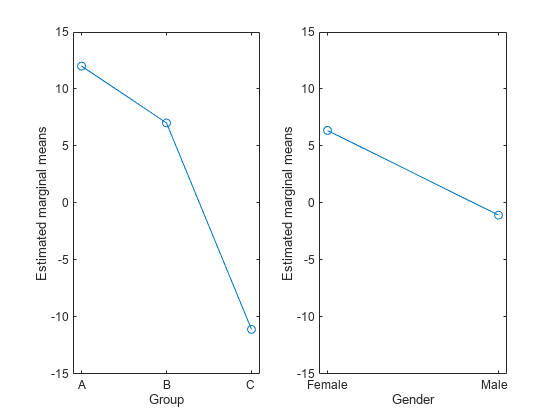
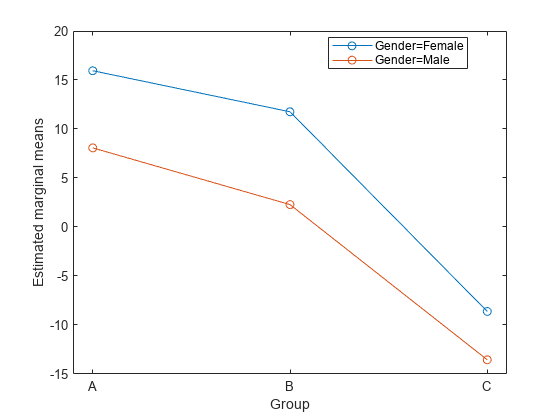
plotprofile
Plot expected marginal means with optional grouping
Description
plotprofile(
specifies additional options by one or more name-value arguments. For example, you
can specify the factors to group by or change the line colors.rm,X,Name,Value)
H = plotprofile(___)H to the plotted lines.